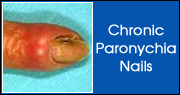
Chronic Paronychia Nails

A chronic paronychia is an infection that usually develops slowly, causing gradual swelling, tenderness and redness of the skin around the nails. It is usually caused by Candida or some other species of fungus (an organism similar to mushrooms, molds and mildew), and it often affects several fingers on the same hand. People with a higher-than-average risk for chronic paronychia include those with diabetes or workers whose jobs constantly expose their hands to water or chemical solvents. Such jobs include bartending, house cleaning, janitorial work, dentistry, nursing, food service, dishwashing and hairdressing.
There are three distinct varieties:
The chronic paronychia is most commonly seen with the "ingrown toenail" with chronic inflammation, thickening and purulence of the eponychial fold and loss of the cuticle. There may or may not be granulation tissue. This also occurs with individuals whose hands are frequently exposed to moisture and minor trauma.
The acute paronychia almost always involves fingers and is much more painful. It is caused by the introduction of pyogenic bacteria by minor trauma and results in acute inflammation and abscess formation within the thin subcutaneous layer between the skin of the eponychial fold and the germinal layer of the eponychial cul- de-sac. In its earliest subacute form there may only be cellulitis with no collection of pus.
The third variety of paronychia is a subungual abscess, which occurs in the same location as a subungual hematoma, between the nail plate and the nail bed.
Choose a Nail Condition














 Dr Foot Recommends
Dr Foot Recommends



















